IRQB Insights: What is Turtle Diagram?
IRQB Insights is an article series showcasing and introducing various technical aspects of rail quality and the IRIS Certification scheme. It helps to explain some and provide insight into the operational matters of the certificate and quality management without requiring prior knowledge to understand the articles.
IRIS Certification rules require many processes to be visually systematised by using Turtle Diagrams. The charming name of the diagram comes from the placement of the information on the scheme where parts of information are gathered around one central body forming the shape of a turtle.
Turtle Diagrams are used for representing various processes in an organizations business management.
It is highly recommended to display at least the five main mandatory processes according to the IRIS certification Conformity Assessment in a turtle diagram.
These five processes are:
- Requirements management
- Project management
- Control of externally provided processes, products and services (EPPPS)
- Design and development
- Production and service provision
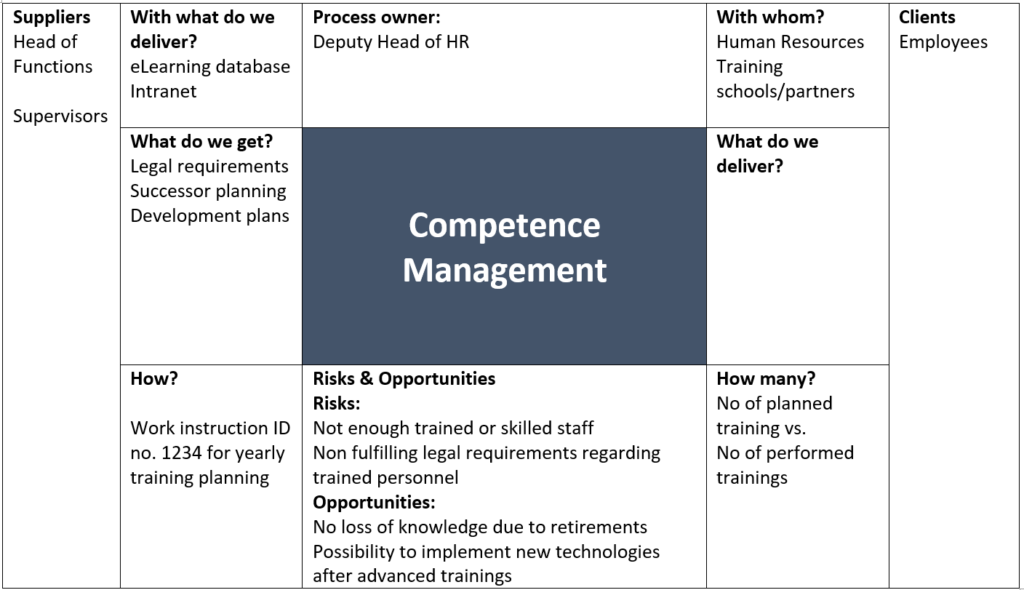
In this article, we will be taking the example of competence management to describe how to build up a Turtle Diagram.
Turtle Diagram is built up through answering to a series of questions that guide you to fill in the correct information to each of the sections:
- What do we get? (middle left on diagram)
- What do we deliver? (middle right on diagram)
- With what do we deliver? (top left on diagram)
- Who are the process owners? (top centre on diagram)
- Who is involved in the process and who is affected by it? (top right on diagram)
- How can I measure the effectiveness and achievement of the process objectives using key figures? (bottom right on diagram)
- Which methods, procedures and instructions should be used and what information is available? (bottom left on diagram)
- Who are the suppliers? (along the left side)
- Who are the customers? (along the right side)
- What are the risks & opportunities? (bottom centre on diagram)